1.About the WC-Co (Carbide)
Summary of WC-Co (Carbide)
The WC-Co (Carbide) is the generic name for certain metal that is combined with a tungsten carbide (WC) and a cobalt (Co) which is a binder and sinters at a high temperature and produced.
Generally, it is considered to have the hardness next to the diamond, but it can be changed the ratio of WC and Co depending on some usages and can be changed the characteristic.
It can be changed a characteristic by adding Ni or the Cr, and the materials manufacturer develops various types of WC-Co (Carbide).
The WC-Co (Carbide) without Co is also developed.
The WC-Co (Carbide) is mainly used as materials of a field required the abrasion resistance and the impact resistance characteristics such as a cutting tool or the die. We would choose any type of WC-Co (carbide) depending on the specifications of the customer.
The History of WC-Co (Carbide)
| 1909 | Developed by GE (U.S.A.) |
|---|---|
| 1923 | Osram AG (German) acquires the patent |
| 1929 | Krupp (ThyssenKrupp AG German) named as “WIDIA” and launched |
| 1927 | Siburan Company (now is Toshiba Company) And Tokyo Denki Company is the first company in Japan to development Tungsten Carbide. |
Characteristic of WC-Co (Carbide)
- Quite hard (HRA80 to 95)
- Although the WC-Co(Carbide) is a kind of brittle material which might be breakabke depending on the stress of adding load and/or power , but is tenacious for hardness
- By changing a particle size and quantity of Co, its hardness could be settled as sticky super hard.
- High Specific Gravity (13 to 15g/㎤)
- Very expensive than the dies steel and the HSS steel
Processing Properties of WC-Co (Carbide)
- Because it is manufactured from powder, it can be easily produce even one
- It eliminated need for the hardening or the tempering
- The sinker and wire cut electric discharge machining can be available
- Using the diamond tool for cutting work or grinding work
2.About the Tungsten Carbide Heading Dies
Historic Development of Tungsten Carbide Heading Dies
The emeritus professor at Osaka University Kozo Osakada stated as follows.
“The WC-Co (Carbide) was developed as the materials for the drawing dies. It is not clear that when is the beginning age to use the WC-Co (Carbide) to the cold forging, but it is thought that it was used from very begining (about the year 1940) of developping the cold forging in Germany.
The tungsten carbide tool was known in Japan, but the dies steel (SKD11) was the majority in the 1960s. After the 1980s, it came to often use the high-speed steel (HSS) and the WC-Co (Carbide). The precision of the cold forging product comes to have much use of the WC-Co (Carbide) for the purpose of the product precision improvement recently to be influenced by the elastic deformation of the tool greatly ”
Above tendency is remarkable in the cold heading process, and there comes to a certain assessment that the WC-Co (carbide) is absolutely indispensable.
Our Tungsten Carbide Heading Dies and Punches
Among the heading dies producing in us, we would explain the three typical structure of dies and the manufacturing method of them.
General Heading Dies
Usually, the heading dies has the structure of the WC-Co (Carbide) with the dies steel which reinforcing the WC-Co(Carbide).
Since the WC-Co (Carbide) is bristtle materials and very expensive, all dies might not be made of the WC-Co (Carbide).
We produce the die material by making a hole to the dies steel and then into that hole inside implementing with the shrinkage fit and press fit
Then, we would do the hole processing with the small hole electric discharge machining, the wire cut electric discharge machining and the sinker electric discharge machining to the WC-Co (Carbide) part. This part becomes the core where, actually, is used for the component production. Therefore, we finish it in a mirror surface condition by the lap processing in the hole inside. Depending on its quality, the life-time of the die could be changed several times more. Even if it is said that the lap processing records life on a die, that is no exaggeration.
 The Heading Dies for Micro parts
The Heading Dies for Micro parts
Assembled Die
In addition, we would be able to plan cost reduction by making the structure that can change only the portion of the WC-Co (Carbide) where wearing out.
We call the assembled dies that comprised of such a plural materials in us. What kind of die structure we take is the capability that is tested asr the die manufacturer is tested.
 Various Heading Dies and Punches
Various Heading Dies and Punches
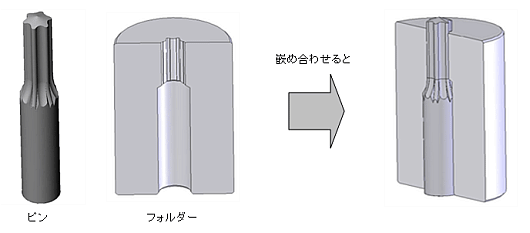
Tungsten Carbide Two-piece Punch
The tungsten carbide die which is divided into a pin and folder whichsets that pin
As for the Integral custructioned shape with the pin and the folder, the stress is concentrated at the root of the pin. Then the die might be disrupted on that area. The tungsten carbide two-piece punch is suitable for mass production of stainless hexalobular shape head screw which could prevent very strong stress to the dies. Because the hexalobular shape head, not like plus or minus shape, is very difficult to form due to unique shape of hexalobular. And it would exercise its performance for mass production of such a complexed shape as a result. In general the HSS all-in-one punch is used for that production, but the life-time of the dies goes short. On the other hand the life-time of the tungsten carbide two-piece punch would be 15 times to 30 times than HSS one and even if a pin is worn, you will be able to sharpen it again and reuse it.
When there is gap between a pin and the folder at the time of header processing, the burr might come out to a product. In order to solve that problem, after having produced pins, we measure the shape of pin by the 3D measuring device and produce folders based on the data. Because we would be able to suppress the gap to around several μm, any burr do not occur.
 Hexalobular Shape Two-piece Punch
Hexalobular Shape Two-piece Punch